Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy ( PEG )
PEG | Purpose | Complications | Advantages
What is percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG)?
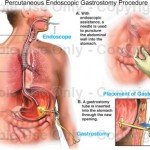
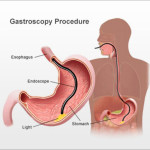
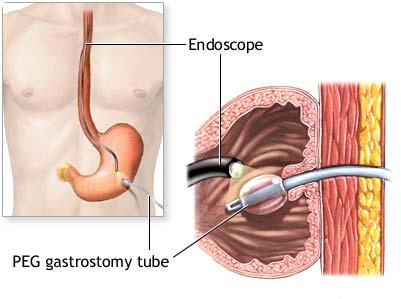
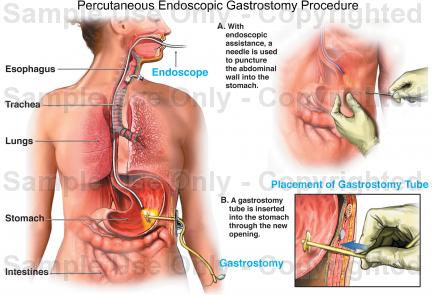
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is a surgical procedure for placing a feeding tube without having to perform an open operation on the abdomen (laparotomy). A gastrostomy (a surgical opening into the stomach) is made percutaneously (through the skin) using an endoscope (a flexible, lighted instrument) to determine where to place the feeding tube in the stomach and secure it in place.
Who does PEG?
PEG is done by a doctor. The doctor may be a general surgeon, an otolaryngologist (ENT specialist), a gastroenterologist (GI specialist), etc.
Where is PEG done?
PEP is performed in a hospital or outpatient surgical facility.
How is PEG done?
Local anesthesia (usually lidocaine or another spray) is used to anesthetize the throat. An endoscope (a flexible, lighted instrument) is passed through the mouth, throat and esophagus to the stomach. The doctor then makes a small incision (cut) in the skin of the abdomen and pushes an intravenous cannula (an IV tube) through the skin into the stomach and sutures (ties) it in place.
When can the PEG patient go home?
The patient can usually go home the same day or the next morning.
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy At A Glance
- PEG is a surgical procedure.
- PEG is a method of providing fluids and nutrition.
- PEG is typically performed using local anesthesia